Unlocking The Secrets Of The Circadian Dead Zone: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever felt an inexplicable drop in energy during certain hours of the day, no matter how much rest you’ve had? This could be the result of your circadian dead zone, a fascinating yet often overlooked aspect of our biological rhythm. The circadian dead zone refers to a specific period in our 24-hour cycle when our bodies are least responsive to external stimuli, making us feel sluggish or unmotivated. Understanding this phenomenon can help us optimize our daily routines and improve our overall well-being.
Our internal body clock, or circadian rhythm, regulates various physiological processes, including sleep-wake cycles, hormone release, and body temperature. While most people are familiar with terms like "morning person" or "night owl," few realize that the circadian dead zone plays a crucial role in how we function throughout the day. This period, often occurring in the early afternoon, is when our alertness and cognitive performance naturally dip, leaving us vulnerable to fatigue and decreased productivity.
Despite its importance, the circadian dead zone remains a mystery to many. By exploring its causes, effects, and potential solutions, we can better manage this biological phenomenon and harness its power for a healthier, more balanced life. In this article, we’ll delve deep into the science behind the circadian dead zone, uncover its impact on daily life, and provide actionable strategies to mitigate its effects. Whether you’re a student, professional, or stay-at-home parent, understanding this concept can transform the way you approach your day.
Read also:Tuumlrk Swinger Exploring The Lifestyle And Community
Table of Contents
- What is the Circadian Dead Zone?
- Why Does the Circadian Dead Zone Matter?
- How to Identify Your Circadian Dead Zone?
- What Are the Effects of the Circadian Dead Zone?
- How Can You Overcome the Circadian Dead Zone?
- What Role Does Light Play in Circadian Rhythm?
- How to Optimize Your Daily Routine Around the Circadian Dead Zone?
- FAQs About the Circadian Dead Zone
What is the Circadian Dead Zone?
The circadian dead zone is a period during the day when your body’s internal clock is least responsive to external stimuli, leading to a noticeable decline in energy and focus. This phenomenon is a natural part of the circadian rhythm, the internal process that regulates our sleep-wake cycle and other physiological functions. Typically occurring in the early afternoon, the circadian dead zone is characterized by a temporary dip in alertness and productivity.
During this time, your body’s core temperature drops slightly, and melatonin levels may rise, even if you’re awake. These changes can make you feel sluggish, unmotivated, or even irritable. While the exact timing and duration of the circadian dead zone vary from person to person, it generally aligns with the post-lunch slump that many people experience between 1 PM and 3 PM.
Understanding the circadian dead zone is crucial for managing daily tasks and maintaining productivity. By recognizing when this period occurs in your schedule, you can adjust your activities to minimize its impact. For example, scheduling less demanding tasks during this time or incorporating short breaks can help you stay on track. Additionally, knowing about the circadian dead zone allows you to make informed decisions about sleep, diet, and exercise, all of which influence your overall circadian rhythm.
What Causes the Circadian Dead Zone?
The circadian dead zone is primarily caused by fluctuations in your body’s internal clock, which is influenced by various factors such as light exposure, meal timing, and sleep patterns. One of the key drivers is the natural ebb and flow of hormones like cortisol and melatonin. Cortisol, which promotes wakefulness, tends to decrease in the early afternoon, while melatonin, which induces sleepiness, begins to rise.
Light exposure also plays a significant role. During the day, bright light signals your brain to stay alert, but as light levels diminish in the afternoon, your body may interpret this as a cue to wind down. This is particularly true for individuals working in dimly lit environments or those who spend long hours indoors.
Other contributing factors include meal timing and composition. Heavy, carbohydrate-rich lunches can exacerbate the effects of the circadian dead zone by causing blood sugar spikes followed by crashes. Similarly, inadequate sleep or irregular sleep schedules can disrupt your circadian rhythm, making the dead zone more pronounced.
Read also:Noa Tishby The Multifaceted Star Who Redefined Entertainment
How Does the Circadian Dead Zone Differ from Sleep Inertia?
While the circadian dead zone and sleep inertia both involve temporary declines in alertness, they are distinct phenomena. Sleep inertia refers to the grogginess and disorientation experienced immediately after waking up, whereas the circadian dead zone occurs later in the day and is unrelated to sleep transitions. Understanding this distinction is essential for addressing each issue effectively.
Why Does the Circadian Dead Zone Matter?
The circadian dead zone matters because it has a profound impact on both physical and mental performance. During this period, your ability to concentrate, make decisions, and complete tasks efficiently is significantly reduced. This can lead to decreased productivity, increased errors, and even accidents in high-stakes environments such as driving or operating machinery.
From a health perspective, consistently ignoring the circadian dead zone can contribute to chronic fatigue, stress, and burnout. Over time, these effects may exacerbate underlying health conditions or lead to new ones, such as insomnia, anxiety, or metabolic disorders. By acknowledging and addressing the circadian dead zone, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your well-being and enhance your quality of life.
Why Should You Pay Attention to Your Circadian Rhythm?
Paying attention to your circadian rhythm, including the circadian dead zone, is essential for maintaining balance and achieving optimal performance. Your circadian rhythm influences not only your sleep but also your mood, immune function, and even your risk of chronic diseases. Disruptions to this rhythm, whether due to shift work, jet lag, or poor sleep habits, can have far-reaching consequences.
By aligning your daily activities with your natural circadian rhythm, you can maximize your energy levels, improve cognitive function, and reduce the likelihood of burnout. For instance, scheduling mentally demanding tasks during your peak alertness periods and reserving lighter activities for the circadian dead zone can help you work smarter, not harder.
How Does the Circadian Dead Zone Affect Mental Health?
The circadian dead zone can also impact mental health by contributing to feelings of frustration, irritability, and low motivation. These emotional responses are often compounded by societal expectations to maintain constant productivity, regardless of natural energy fluctuations. Over time, this mismatch between biological needs and external demands can lead to anxiety, depression, or other mental health challenges.
How to Identify Your Circadian Dead Zone?
Identifying your circadian dead zone requires paying close attention to your body’s natural energy patterns throughout the day. Start by keeping a daily journal to track your energy levels, mood, and productivity. Note the times when you feel most alert and focused, as well as when you experience dips in energy or motivation.
Another effective method is to use wearable technology or apps designed to monitor sleep and activity patterns. These tools can provide insights into your circadian rhythm and help pinpoint when your circadian dead zone occurs. Additionally, observing how external factors such as meals, exercise, and light exposure influence your energy levels can offer valuable clues.
What Are the Signs of a Circadian Dead Zone?
Common signs of a circadian dead zone include yawning, difficulty concentrating, reduced motivation, and a strong desire to nap. You may also notice physical symptoms such as headaches, muscle stiffness, or a general sense of lethargy. Recognizing these signs can help you anticipate and prepare for the circadian dead zone, minimizing its impact on your day.
How Can Technology Help Identify Your Circadian Dead Zone?
Modern technology offers several tools to help identify your circadian dead zone. Wearable devices like fitness trackers and smartwatches can monitor metrics such as heart rate variability, sleep quality, and activity levels, providing a comprehensive view of your circadian rhythm. Similarly, apps that track sleep cycles and energy patterns can offer personalized insights and recommendations for optimizing your daily routine.
What Are the Effects of the Circadian Dead Zone?
The effects of the circadian dead zone extend beyond temporary fatigue, influencing various aspects of daily life. One of the most immediate impacts is reduced productivity, as the decline in alertness and focus makes it challenging to complete tasks efficiently. This can lead to missed deadlines, poor performance, and increased stress levels.
Physically, the circadian dead zone can manifest as muscle tension, headaches, or digestive issues, particularly if you consume heavy meals during this time. Mentally, it can contribute to feelings of frustration, irritability, and low motivation, affecting your interactions with others and your overall mood.
Long-term, consistently ignoring the circadian dead zone can disrupt your sleep-wake cycle, leading to chronic fatigue and an increased risk of health conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. By addressing this phenomenon proactively, you can mitigate its effects and improve your overall well-being.
What Are the Long-Term Consequences of Ignoring the Circadian Dead Zone?
Ignoring the circadian dead zone over time can have serious long-term consequences. Chronic fatigue, for example, can impair immune function, leaving you more susceptible to illnesses. It can also disrupt hormonal balance, increasing the risk of conditions such as insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome.
From a mental health perspective, consistently pushing through the circadian dead zone without adequate rest can lead to burnout, anxiety, and depression. The cumulative stress of trying to maintain high performance during low-energy periods can take a toll on both your physical and emotional health.
How Does the Circadian Dead Zone Affect Physical Health?
The circadian dead zone can negatively impact physical health by disrupting metabolic processes and increasing inflammation. For instance, consuming large meals during this time can lead to poor digestion and weight gain, while inadequate rest can impair muscle recovery and repair. Over time, these effects can contribute to chronic health issues and reduce overall quality of life.
How Can You Overcome the Circadian Dead Zone?
Overcoming the circadian dead zone requires a combination of lifestyle adjustments, strategic planning, and self-awareness. One of the most effective strategies is to align your daily schedule with your natural energy patterns. For example, schedule demanding tasks during your peak alertness periods and reserve lighter activities for the circadian dead zone.
Incorporating short breaks or power naps during the circadian dead zone can also help recharge your energy levels. A 10-20 minute nap can boost alertness and improve cognitive function without interfering with nighttime sleep. Additionally, staying hydrated, eating balanced meals, and engaging in light physical activity can mitigate the effects of the circadian dead zone.
What Are Some Practical Tips for Managing the Circadian Dead Zone?
Here are some practical tips for managing the circadian dead zone:
- Take a short walk or stretch to boost circulation and energy levels.
- Consume light, protein-rich snacks instead of heavy meals.
- Expose yourself to natural light to reset your internal clock.
- Practice mindfulness or deep breathing exercises to reduce stress.
- Use tools like timers or apps to remind you to take breaks.
How Can Light Therapy Help Overcome the Circadian Dead Zone?
Light therapy is a powerful tool for overcoming the circadian dead zone by resetting your internal clock and boosting alertness. Exposure to bright light, particularly in the morning, can help regulate your circadian rhythm and reduce the severity of the circadian dead zone. Specialized light therapy devices, such as lightboxes, mimic natural sunlight and can be used at home or in the workplace.
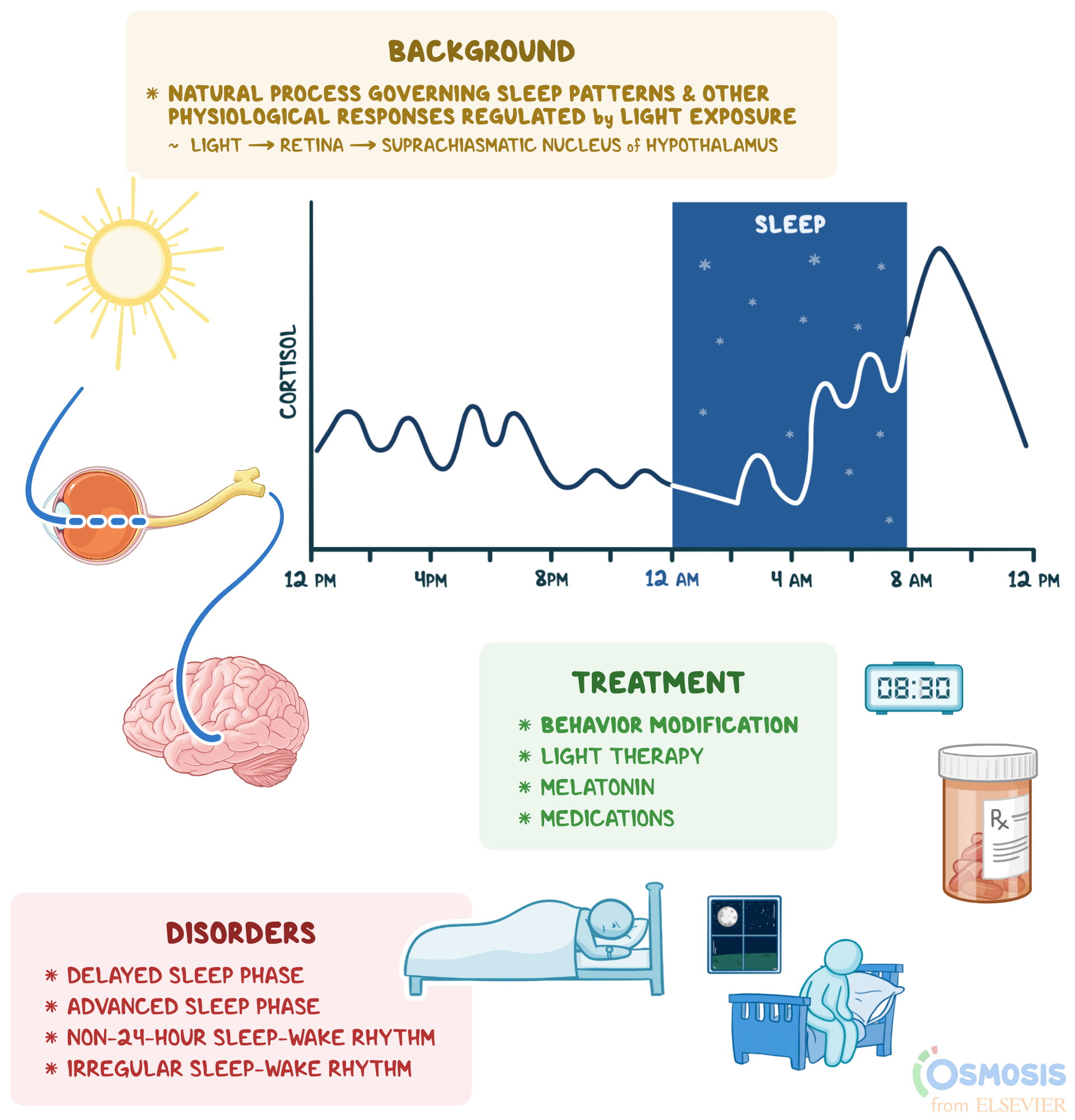
What Role Does Light Play in Circadian Rhythm?
Light is one of the most critical factors influencing the circadian rhythm. It serves as the primary external cue that signals your brain when to wake up and when to wind down. Exposure to bright light in the morning helps synchronize your internal clock, while dim light in the evening prepares your body for sleep.
During the circadian dead zone, reduced light exposure can exacerbate feelings of
Foolio Autopsy Uncensored: Uncovering The Truth Behind The Controversy
What Is An Archive Eraser And Why Should You Care?
Kevin Anderson Climate: Understanding The Expert’s Insights On Global Warming
Circadianrhythm designs, themes, templates and downloadable graphic
Circadian Rhythm What Is It, How It Works, Why It’s Important, and